Understanding pharmacy school enrollment decline
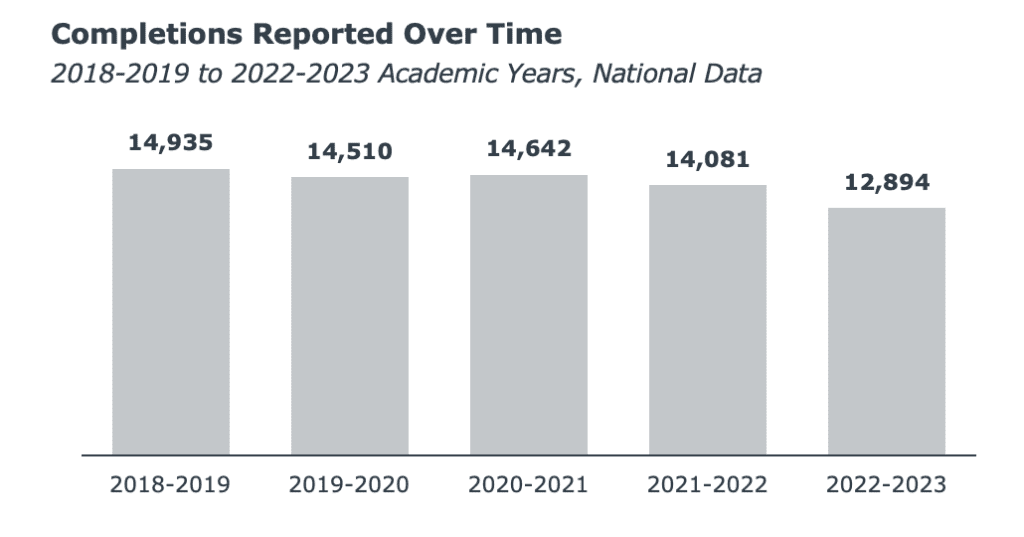
PharmD programs are grappling with a steady decline in student demand. Through an analysis of IPEDS data, our team found that completions have dropped by roughly 2,000 nationwide over the past few years. Despite a brief recovery in 2020-2021 the downward trend has persisted, with competition slightly increasing as more institutions offer PharmD programs.
With shrinking class sizes and fewer students entering the field, the outlook for pharmacy programs is becoming increasingly challenging. The rise of online prescription services, stagnant wage growth, and a slower-than-average employment projection for pharmacists only adds to the concerning long-term outlook. Explore two reasons why you may be struggling to reach your pharmacy school enrollment goals.
Declining Student Demand and Rising Competition
PharmD programs are suffering from a decrease in student demand overall. Pharmacy school application decline has been a significant factor contributing to this trend, with completions decreasing nearly every year from 2018 to 2023, ultimately experiencing a decline of over 2,000 degree completions.
See this pharmacy school’s tactic for growing enrollment
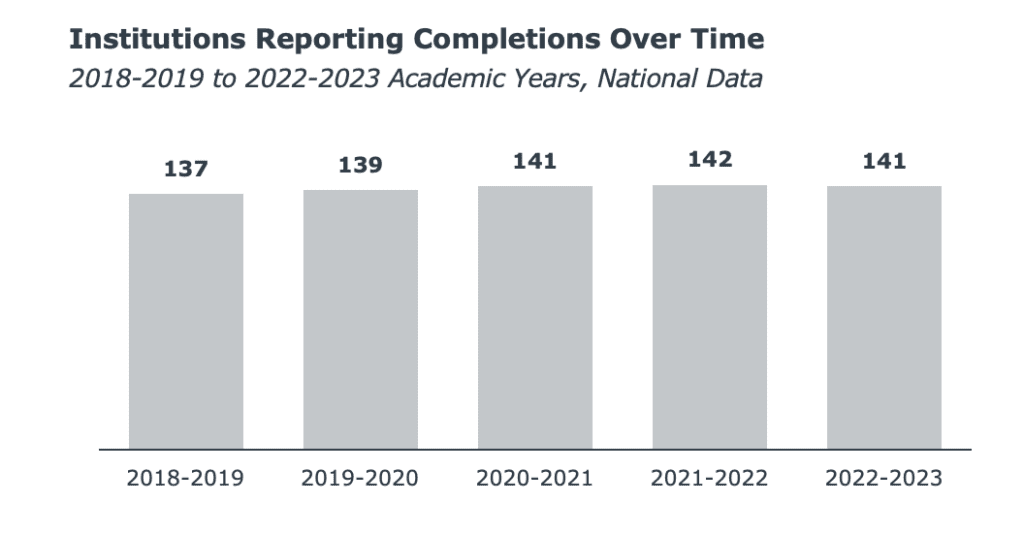
At the same time, competition is on the rise. The number of institutions reporting PharmD completions increased by four from the 2018-2019 and 2022-2023 academic years (137 to 141).
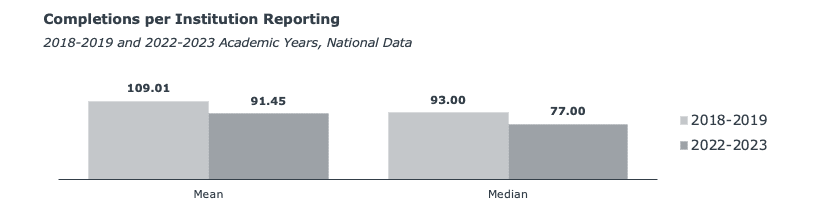
Declining PharmD completions amid slightly increasing competition has led to shrinking class sizes. The mean and median completions per institution declined between the 2018-2019 and 2022-2023 academic years from about 109 (mean) and 93 (median) to now hovering at about 91 (mean) and 77 (median).
Here’s how one pharmacy school grew enrollment by 23%, despite rising competition
How job market changes and income stagnation are impacting pharmacists
Although demand is projected to increase for pharmacists in some health care settings (e.g., hospitals, clinics), many pharmacists work in retail pharmacies (e.g., drug stores, supermarkets). Fewer pharmacist jobs are expected in these retail facilities as more people fill their prescriptions online or by mail.
Further, growth in pharmacist income is projected to lag behind other health professions in the near future, based on analysis of 10-year income trends for pharmacists between 2012 to 2021. Individuals, organizations, and professional bodies are trying to create opportunities for income growth, but the projected income lag persists.
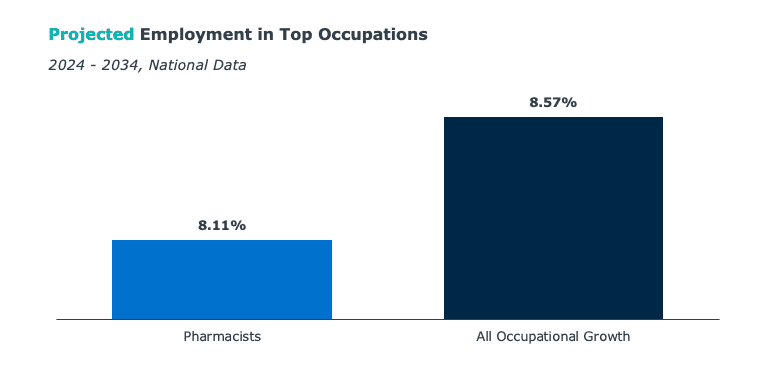
National employment for pharmacists is projected to increase slower than average for all occupations across the next decade. This suggests employment opportunities for program graduates will likely grow at a slower rate in the coming years.
How to Compete in this Declining and Competitive Market
Pharmacy school enrollment decline, driven by slow-growing income and a negative projected employment outlook for pharmacists, presents a challenging problem. However, you can increase your program’s appeal to prospective students by integrating fundamental skills (e.g., workflow management, loss prevention) and emerging skills (e.g., data analysis, business metrics) into PharmD curricula.
Skills Scatterplot
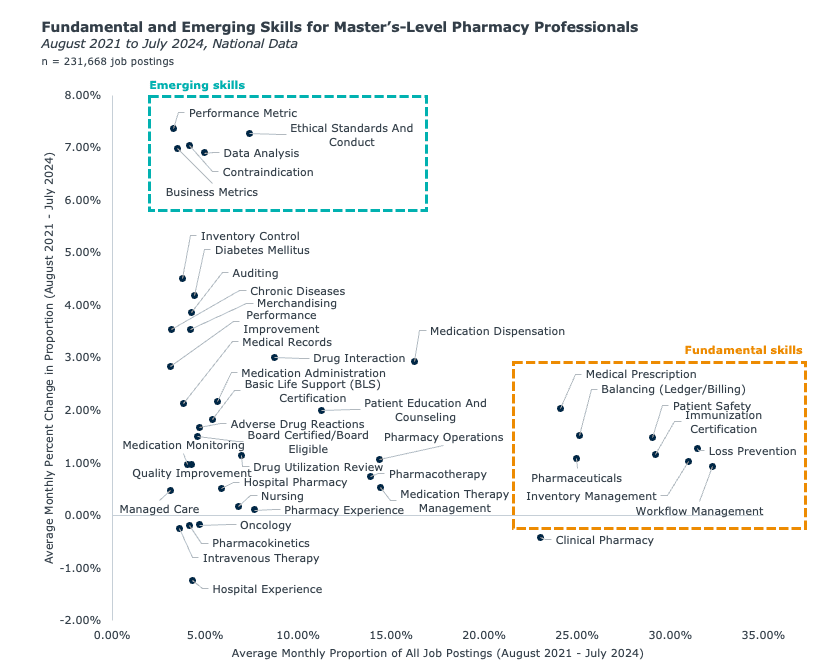
Pharmacy schools can expand patient management, leadership and management training, and technology skills to address changes in the pharmacy market.
Additionally, pharmacy schools can enhance their use of targeted marketing strategies to better attract students, especially as the number of students taking the PCAT declines. While word-of-mouth remains an important aspect of pharmacy recruitment, utilizing effective marketing techniques to engage prospective students early on can significantly boost the likelihood of them applying to your program.
Despite the challenges and hurdles that exist, there are opportunities for PharmD programs to adapt their curricula and sharpen their marketing to attract students who remain interested in pursuing pharmacy careers.
By prioritizing student needs and adapting to market changes, your institution can thrive despite challenges. Learn how EAB’s Adult Learner Recruitment team can boost your PharmD program for the future.

More Blogs

4 questions domestic students will ask before applying to your graduate program

When Grad PLUS disappears: What 8,000+ grad students said about paying for school
